Move freely; live fully™
WHAT IS OSTEOARTHRITIS (OA)?
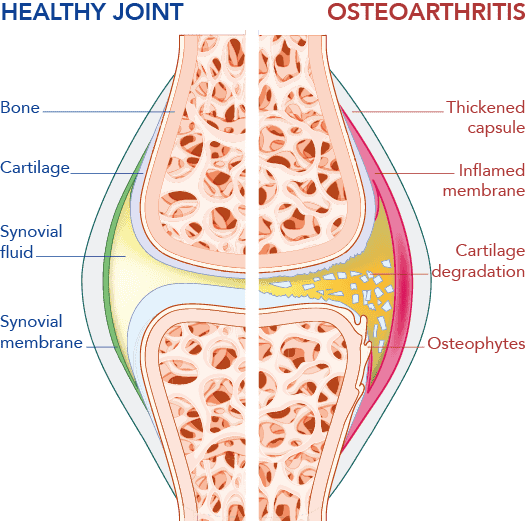
Osteoarthritis, also known as arthrosis, is a condition that affects your joints, leading to the gradual wearing down of the cartilage that normally cushions them. This process can result in changes to the surrounding bone, causing discomfort and limiting your ability to move as freely as you once did.
Common symptoms of osteoarthritis include pain, stiffness, and a reduction in joint mobility. Over time, these symptoms can become more noticeable, sometimes leading to changes in joint shape.
While osteoarthritis can be frustrating, understanding the condition is an important first step in managing it. Some treatments can help reduce pain and improve your ability to stay active, even as you work to protect your joints from further wear and tear.
COMMON SYMPTOMS
Symptoms can vary from day to day, from person to person and also according to the grade of OA. They can often develop slowly and worsen over time.
Loss of flexibility

Pain
Bone Spurs
Tenderness
Grating sensation
Stiffness
SOURCES
1. CDC. Osteoarthritis - www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/osteoarthritis.htm (Accessed 03/2023)
2. OARSI. Patients. Understanding Your Osteoarthritis - oarsi.org/education/patients (Accessed 03/2023)
3. Mayo Clinic. Osteoarthritis - www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoarthritis/symptoms-causes/syc- 20351925 (Accessed 03/2023)
4. Allen KD, et al. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2022; 30(2):184-195
THE IMPACT OF OA
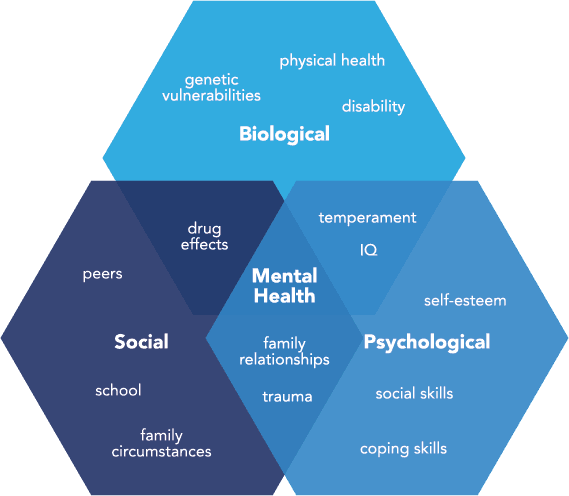
Osteoarthritis (OA) can lead to chronic pain, which is influenced by a mix of factors. These include biological factors like the degree of joint damage, psychological factors such as your thoughts and feelings about OA, and social factors like challenges in exercising or working because of the condition.
Since everyone’s pain is unique, it’s important to take a personalised approach to treatment. Addressing these different factors can help reduce pain, improve your mobility, and enhance your overall quality of life.
Diagnosis
It’s important to seek advice from a healthcare professional as soon as you notice the first signs of OA. Early diagnosis can make a big difference.
Diagnosing OA usually starts with your health specialist looking at your medical history and symptoms, followed by a physical examination.
An X-ray is often needed to confirm the diagnosis. The X-ray can reveal key indicators of OA, such as the presence of bone growths (osteophytes) and a narrowing of the joint space.
Causes of OA
When it comes to the development of osteoarthritis, there are two main types of risk factors:
1. Modifiable Risk Factors: These are preventable and often related to lifestyle, including:
• Excess weight and obesity
• Trauma and joint injuries
• Occupation-related activities
2. Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: These are factors you can’t change, including:
• Genetic predisposition
• Being female
• Advancing age
Understanding these risk factors can help you take steps to manage or reduce your risk of developing OA.
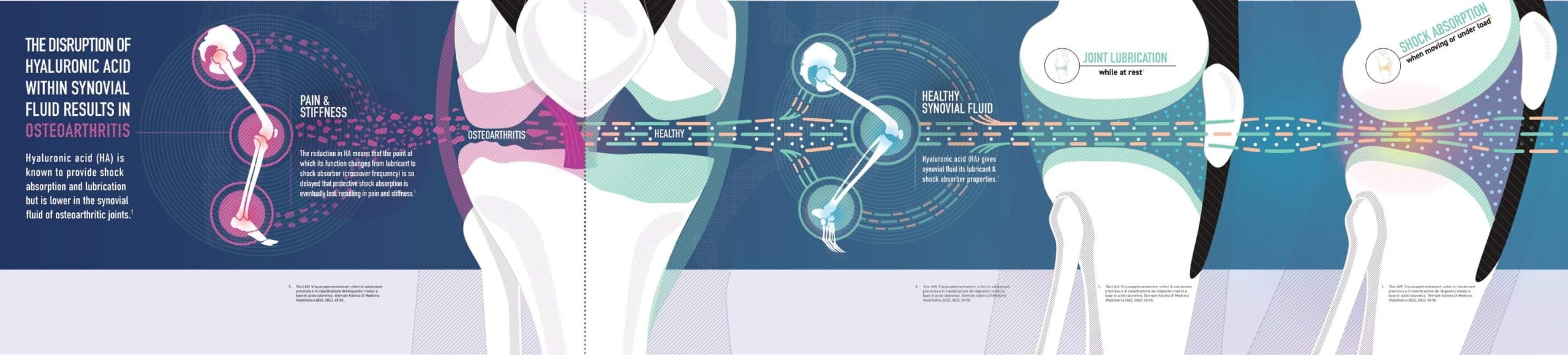
Synovial Fluid
Healthy Synovial Joints: The Body’s Main Functional Joints
Healthy synovial joints contain a cavity filled with synovial fluid, enclosed by an articular capsule. This fluid reduces friction, supports smooth movement, and protects the joint.
Key Functions of Synovial Fluid:
Lubricating Function:
- Reduces friction during joint movement
- Prevents erosion of cartilage and bone surfaces
- Enhances range of motion within joints
Nourishing Function:
- Supplies essential nutrients to articular cartilage
- Removes metabolic waste
Supporting Movement & Load Bearing
- Acts as a shock absorber during weight-bearing activities
- Distributes load evenly across joint surfaces
Synovial fluid is a crucial component of the joints, supporting everyday activities by reducing friction between articular cartilages of synovial joints during movement.
Lifestyle
A healthy diet and physical activity
are important in helping to keep your joints healthy
Treatments
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition that often causes painful flare-ups. Treatment should, therefore, simultaneously manage the pain while slowing down joint degeneration.
Today, new treatments are available that can help repair cartilage, boost the body’s natural healing processes, and effectively manage pain.
Your healthcare professional will recommend the best treatment options for your OA based on the severity and location of your OA. They may also suggest lifestyle changes, such as weight loss if needed and engaging in low-impact aerobic exercises like swimming, aqua aerobics, or cycling to reduce strain on the painful joint while staying active.
Managing osteoarthritis effectively requires a tailored approach based on the severity of your symptoms. From non-pharmacological methods and medications to surgical options, each step is designed to help control pain, improve function, and protect your joints.
The information on the website is for information purposes only and is not to be considered a substitute for medical advice. Ask your doctor for more information.









